
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about Investigating End-to-end ASR Architectures for Long form Audio Transcription
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents an overview and evaluation of some of the end-to-end ASR models on long-form audios. We study three categories of Automatic Speech Recognition(ASR) models based on their core architecture: (1) convolutional, (2) convolutional with squeeze-and-excitation and (3) convolutional models with attention. We selected one ASR model from each category and evaluated Word Error Rate, maximum audio length and real-time factor for each model on a variety of long audio benchmarks: Earnings-21 and 22, CORAAL, and TED-LIUM3.
- Categories:
 2 Views
2 Views
- Read more about DEMUCS for data-driven RF signal denoising
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present our radio frequency signal denoising approach, RFDEMUCS, for the 2024 IEEE ICASSP RF Signal Separation Challenge. Our approach is based on the DEMUCS architecture [1], and has a U-Net structure with a bidirectional LSTM bottleneck. For the task of estimating the underlying bit-sequence message, we also propose an extension of the DEMUCS that directly estimates the bits. Evaluations of the presented methods on the challenge test dataset yield MSE and BER scores of −118.71 and −81, respectively, according to the evaluation metrics defined in the challenge.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views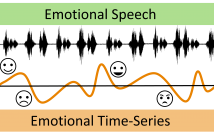
- Read more about Dynamic Speech Emotion Recognition using a Conditional Neural Process
- Log in to post comments
The problem of predicting emotional attributes from speech has often focused on predicting a single value from a sentence or short speaking turn. These methods often ignore that natural emotions are both dynamic and dependent on context. To model the dynamic nature of emotions, we can treat the prediction of emotion from speech as a time-series problem. We refer to the problem of predicting these emotional traces as dynamic speech emotion recognition. Previous studies in this area have used models that treat all emotional traces as coming from the same underlying distribution.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about FEATURE-CONSTRAINED AND ATTENTION-CONDITIONED DISTILLATION LEARNING FOR VISUAL ANOMALY DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Visual anomaly detection in computer vision is an essential one-class classification and segmentation problem. The student-teacher (S-T) approach has proven effective in addressing this challenge. However, previous studies based on S-T underutilize the feature representations learned by the teacher network, which restricts anomaly detection performance.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views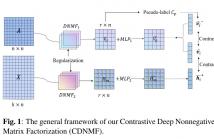
- Read more about [Poster] Contrastive Deep Nonnegative Matrix Factorization For Community Detection
- Log in to post comments
Recently, nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) has been widely adopted for community detection, because of its better interpretability. However, the existing NMF-based methods have the following three problems: 1) they directly transform the original network into community membership space, so it is difficult for them to capture the hierarchical information; 2) they often only pay attention to the topology of the network and ignore its node attributes; 3) it is hard for them to learn the global structure information necessary for community detection.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about [Poster] Contrastive Deep Nonnegative Matrix Factorization For Community Detection
- Log in to post comments
Recently, nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) has been widely adopted for community detection, because of its better interpretability. However, the existing NMF-based methods have the following three problems: 1) they directly transform the original network into community membership space, so it is difficult for them to capture the hierarchical information; 2) they often only pay attention to the topology of the network and ignore its node attributes; 3) it is hard for them to learn the global structure information necessary for community detection.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about ENHANCING NOISY LABEL LEARNING VIA UNSUPERVISED CONTRASTIVE LOSS WITH LABEL CORRECTION BASED ON PRIOR KNOWLEDGE
- Log in to post comments
To alleviate the negative impacts of noisy labels, most of the noisy label learning (NLL) methods dynamically divide the training data into two types, “clean samples” and “noisy samples”, in the training process. However, the conventional selection of clean samples heavily depends on the features learned in the early stages of training, making it difficult to guarantee the cleanliness of the selected samples in scenarios where the noise ratio is high.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Detecting Check-Worthy Claims in Political Debates, Speeches, and Interviews Using Audio Data - Poster
- Log in to post comments
Developing tools to automatically detect check-worthy claims in political debates and speeches can greatly help moderators of debates, journalists, and fact-checkers. While previous work on this problem has focused exclusively on the text modality, here we explore the utility of the audio modality as an additional input. We create a new multimodal dataset (text and audio in English) containing 48 hours of speech from past political debates in the USA.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Detecting Check-Worthy Claims in Political Debates, Speeches, and Interviews Using Audio Data - Presentation
- Log in to post comments
Developing tools to automatically detect check-worthy claims in political debates and speeches can greatly help moderators of debates, journalists, and fact-checkers. While previous work on this problem has focused exclusively on the text modality, here we explore the utility of the audio modality as an additional input. We create a new multimodal dataset (text and audio in English) containing 48 hours of speech from past political debates in the USA.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about TOWARDS MULTI-DOMAIN FACE LANDMARK DETECTION WITH SYNTHETIC DATA FROM DIFFUSION MODEL
- Log in to post comments
Recently, deep learning-based facial landmark detection for in-the-wild faces has achieved significant improvement. However, there are still challenges in face landmark detection in other domains (\eg{} cartoon, caricature, etc). This is due to the scarcity of extensively annotated training data. To tackle this concern, we design a two-stage training approach that effectively leverages limited datasets and the pre-trained diffusion model to obtain aligned pairs of landmarks and face in multiple domains.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views