
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about Synthesizing Black-box Anti-forensics DeepFakes with High Visual Quality
- Log in to post comments
DeepFake, an AI technology for creating facial forgeries, has garnered global attention. Amid such circumstances, forensics researchers focus on developing defensive algorithms to counter these threats. In contrast, there are techniques developed for enhancing the aggressiveness of DeepFake, e.g., through anti-forensics attacks, to disrupt forensic detectors. However, such attacks often sacrifice image visual quality for improved undetectability. To address this issue, we propose a method to generate novel adversarial sharpening masks for launching black-box anti-forensics attacks.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Generalized Multi-Source Inference for Text Conditioned Music Diffusion Models
- Log in to post comments
Multi-Source Diffusion Models (MSDM) allow for compositional musical generation tasks: generating a set of coherent sources, creating accompaniments, and performing source separation. Despite their versatility, they require estimating the joint distribution over the sources, necessitating pre-separated musical data, which is rarely available, and fixing the number and type of sources at training time. This paper generalizes MSDM to arbitrary time-domain diffusion models conditioned on text embeddings.
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about Slide for Interpretable Multimodal Out-of-context Detection with Soft Logic Regularization
- Log in to post comments
The rapid spread of information through mobile devices and media has led to the widespread of false or deceptive news, causing significant concerns in society. Among different types of misinformation, image repurposing, also known as out-of-context misinformation, remains highly prevalent and effective. However, current approaches for detecting out-of-context misinformation often lack interpretability and offer limited explanations. In this study, we propose a logic regularization approach for out-of-context detection called LOGRAN (LOGic Regularization for out-of-context ANalysis).
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about CHANNEL-SPATIAL TRANSFORMER FOR EFFICIENT IMAGE SUPER-RESOLUTION
- Log in to post comments
Transformer has achieved remarkable success in low-level visual tasks, including image super-resolution (SR), owing to its ability to establish global dependencies through self-attention mechanism. However, existing methods overlook the mutual influence and promotion between the channel and spatial dimensions. The feed-forward network (FFN) in the transformer architecture introduces redundant information in the channel during feature extraction, hindering feature representation capability and neglecting spatial information modeling.
poster_1446.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about MULTILINGUAL AUDIO-VISUAL SPEECH RECOGNITION WITH HYBRID CTC/RNN-T FAST CONFORMER
- Log in to post comments
Humans are adept at leveraging visual cues from lip movements for recognizing speech in adverse listening conditions. Audio-Visual Speech Recognition (AVSR) models follow similar approach to achieve robust speech recognition in noisy conditions. In this work, we present a multilingual AVSR model incorporating several enhancements to improve performance and audio noise robustness. Notably, we adapt the recently proposed Fast Conformer model to process both audio and visual modalities using a novel hybrid CTC/RNN-T architecture.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
Advancements in generative algorithms promise new heights in what can be achieved, for example, in the speech enhancement domain. Beyond the ubiquitous noise reduction, destroyed speech components can now be restored—something not previously achievable. These emerging advancements create both opportunities and risks, as speech intelligibility can be impacted in a multitude of beneficial and detrimental ways. As such, there exists a need for methods, materials and tools for enabling rapid and effective assessment of speech intelligibility.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Slides for Renyi Divergences Learning for explainable classification of SAR Image Pairs
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of classifying a pair of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images by proposing an explainable and frugal algorithm that integrates a set of divergences. The approach relies on a statistical framework that takes standard probability distributions into account for modelling SAR data. Then, by learning a combination of parameterized Renyi divergences and their parameters from the data, we are able to classify the pair of images with fewer parameters than regular machine learning approaches while also allowing an interpretation of the results related to the priors used.
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views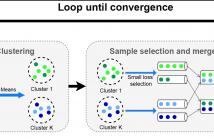
- Read more about Learning with Non-Uniform Label Noise: A Cluster-Dependent Weakly Supervised Approach
- Log in to post comments
Learning with noisy labels is a challenging task in machine learning.
Furthermore in reality, label noise can be highly non-uniform
in feature space, e.g. with higher error rate for more difficult samples.
Some recent works consider instance-dependent label noise
but they require additional information such as some cleanly labeled
data and confidence scores, which are usually unavailable or costly
to obtain. In this paper, we consider learning with non-uniform label
noise that requires no such additional information. Inspired by
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Can Large-scale Vocoded Spoofed Data Improve Speech Spoofing Countermeasure with a Self-supervised Front End?
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
A speech spoofing countermeasure (CM) that discriminates between unseen spoofed and bona fide data requires diverse training data. While many datasets use spoofed data generated by speech synthesis systems, it was recently found that data vocoded by neural vocoders were also effective as the spoofed training data. Since many neural vocoders are fast in building and generation, this study used multiple neural vocoders and created more than 9,000 hours of vocoded data on the basis of the VoxCeleb2 corpus.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Enhancing GAN Performance through Neural Architecture Search and Tensor Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have emerged as a powerful tool for generating high-fidelity content. This paper presents a new training procedure that leverages Neural Architecture Search (NAS) to discover the optimal architecture for image generation while employing the Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) repulsive loss for adversarial training. Moreover, the generator network is compressed using tensor decomposition to reduce its computational footprint and inference time while preserving its generative performance.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views