
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about Boosting Speech Enhancement with Clean Self-Supervised Features Via Conditional Variational Autoencoders
- Log in to post comments
Recently, Self-Supervised Features (SSF) trained on extensive speech datasets have shown significant performance gains across various speech processing tasks. Nevertheless, their effectiveness in Speech Enhancement (SE) systems is often suboptimal due to insufficient optimization for noisy environments. To address this issue, we present a novel methodology that directly utilizes SSFs extracted from clean speech for enhancing SE models. Specifically, we leverage the clean SSFs for latent space modeling within the Conditional Variational Autoencoder (CVAE) framework.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views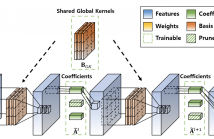
- Read more about G-SharP: Globally Shared Kernel with Pruning for Efficient CNNs
- Log in to post comments
Filter Decomposition (FD) methods have gained traction in compressing large neural networks by dividing weights into basis and coefficients. Recent advancements have focused on reducing weight redundancy by sharing either basis or coefficients stage-wise. However, traditional sharing approaches have overlooked the potential of sharing basis on a network-wide scale. In this study, we introduce an FD technique called G-SharP that elevates performance by using globally shared kernels throughout the network.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Unsupervised Relapse Detection using Wearable-Based Digital Phenotyping for The 2nd E-Prevention Challenge
- Log in to post comments
This paper describes SRCB-LUL team's unsupervised relapse detection system submitted to the 2nd E-Prevention Challenge (Psychotic and Non-Psychotic Relapse Detection using Wearable-Based Digital Phenotyping). In our system, a person identification task is added to make the feature extraction network better distinguish between different behavior patterns. Three different structures of the feature extraction network are adopted. Then, the extracted features are used to train an Elliptic Envelope model of each patient for anomaly detection.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about slides for av2wav
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Speech enhancement systems are typically trained using pairs of clean and noisy speech. In audio-visual speech enhancement
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Importance Sampling Based Unsupervised Federated Representation Learning
- Log in to post comments
The use of AI has led to the era of pervasive intelligence, marked by a proliferation of smart devices in our daily lives. Federated Learning (FL) enables machine learning at the edge without having to share user-specific private data with an untrusted third party. Conventional FL techniques are supervised learning methods, where a fundamental challenge is to ensure that data is reliably annotated at the edge. Another approach is to obtain rich and informative representations ofunlabeled data, which is suitable for downstream tasks.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Privacy Preserving Federated Learning from Multi-input Functional Proxy Re-encryption
- Log in to post comments
Federated learning (FL) allows different participants to collaborate on model training without transmitting raw data, thereby protecting user data privacy. However, FL faces a series of security and privacy issues (e.g. the leakage of raw data from publicly shared parameters). Several privacy protection technologies, such as homomorphic encryption, differential privacy and functional encryption, are introduced for privacy enhancement in FL. Among them, the FL frameworks based on functional encryption better balance security and performance, thus receiving increasing attention.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views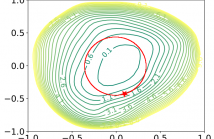
- Read more about BRINGING THE DISCUSSION OF MINIMA SHARPNESS TO THE AUDIO DOMAIN: A FILTER-NORMALISED EVALUATION FOR ACOUSTIC SCENE CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
The correlation between the sharpness of loss minima and generalisation in the context of deep neural networks has been subject to discussion for a long time. Whilst mostly investigated in the context of selected benchmark data sets in the area of computer vision, we explore this aspect for the acoustic scene classification task of the DCASE2020 challenge data. Our analysis is based on two-dimensional filter-normalised visualisations and a derived sharpness measure.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Flattening Singular Values of Factorized Convolution for Medical Images
- Log in to post comments
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have long been the paradigm of choice for robust medical image processing (MIP). Therefore, it is crucial to effectively and efficiently deploy CNNs on devices with different computing capabil- ities to support computer-aided diagnosis. Many methods employ factorized convolutional layers to alleviate the bur- den of limited computational resources at the expense of expressiveness.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Personalised Anomaly Detectors and Prototypical Representations for Relapse Detection from Wearable-Based Digital Phenotyping
- Log in to post comments
We describe our contribution to the 2nd e-Prevention challenge, which focuses on the unsupervised non-psychotic (Track 1) and psychotic (Track 2) relapse detection using wearable-based digital phenotyping. We exploit the measurements gathered from the gyroscope, the accelerometer, and the heart rate-related sensors embedded in a smartwatch. We also include the available sleep information in our experiments. Four dedicated autoencoders are trained to learn embedded representations from each one of the considered modalities.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Tunisian Code Switched ASR Presentation
- Log in to post comments
Crafting an effective Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) solution for dialects demands innovative approaches that not only address the data scarcity issue but also navigate the intricacies of linguistic diversity. In this paper, we address the aforementioned ASR challenge, focusing on the Tunisian dialect. First, textual and audio data is collected and in some cases annotated.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views