
- Read more about THE SLIDE OF WEAKLY SUPERVISED POINT CLOUD UPSAMPLING VIA OPTIMAL TRANSPORT
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about SERAB: A MULTI-LINGUAL BENCHMARK FOR SPEECH EMOTION RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
The Speech Emotion Recognition Adaptation Benchmark (SERAB) is a new framework to evaluate the performance and generalization capacity of different approaches for utterance-level SER. The benchmark is composed of nine datasets for SER in six languages. We used the proposed framework to evaluate a selection of standard hand-crafted feature sets and state-of-the-art DNN representations. The results highlight that using only a subset of the data included in SERAB can result in biased evaluation, while compliance with the proposed protocol can circumvent this issue.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
Convolutional Neural Networks have been extensively used for solving many vision problems. However, due to high memory and computational requirements, deployment of these models on edge devices is limited. Many embedded friendly models such as MobileNet, ShuffleNet, SqueezeNet, and many more are proposed to serve this purpose. But these models are still not compact enough to deploy on edge devices. The popular metric-based pruning methods (which are aimed at pruning insignificant and redundant filters) could achieve limited compression for embedded friendly models such as MobileNet.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views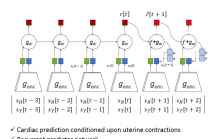
- Read more about Contrastive Predictive Coding for anomaly detection of fetal health from the cardiotocogram
- Log in to post comments
Fetal well-being during labor is currently assessed by medical professionals through visual interpretation of the cardiotocogram (CTG), a simultaneous recording of Fetal Heart Rate (FHR) and Uterine Contractions (UC). This method is disputed due to high inter- and intra-observer variability and a resulting increase in the number of unnecessary interventions. A method for computerized interpretation of the CTG, based on Contrastive Predictive Coding (CPC) is presented here.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about FilterAugment: An Acoustic Environmental Data Augmentation Method
- Log in to post comments
Acoustic environments affect acoustic characteristics of sound to be recognized by physically interacting with sound wave propagation. Thus, training acoustic models for audio and speech tasks requires regularization on various acoustic environments in order to achieve robust performance in real life applications. We propose FilterAugment, a data augmen-tation method for regularization of acoustic models on vari-ous acoustic environments.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Differentiable Programming a la Moreau
- Log in to post comments
The notion of a Moreau envelope is central to the analysis of first-order optimization algorithms for machine learning and signal processing. We define a compositional calculus adapted to Moreau envelopes and show how to apply it to deep networks, and, more broadly, to learning systems equipped with automatic differentiation and implemented in the spirit of differentiable programming.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about Personalized PageRank Graph Attention Networks
- Log in to post comments
There has been a rising interest in graph neural networks (GNNs) for representation learning over the past few years. GNNs provide a general and efficient framework to learn from graph-structured data. However, GNNs typically only use the information of a very limited neighborhood for each node to avoid over-smoothing. A larger neighborhood would be desirable to provide the model with more information.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about One-class Learning Towards Synthetic Voice Spoofing Detection (Poster)
- Log in to post comments
Human voices can be used to authenticate the identity of the speaker, but the automatic speaker verification (ASV) systems are vulnerable to voice spoofing attacks, such as impersonation, replay, text-to-speech, and voice conversion. Recently, researchers developed anti-spoofing techniques to improve the reliability of ASV systems against spoofing attacks. However, most methods encounter difficulties in detecting unknown attacks in practical use, which often have different statistical distributions from known attacks.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about Information Preserving Dimensionality Reduction for Mutual Information Analysis of Deep Learning
- Log in to post comments
Mutual information has been actively investigated as a tool for analyzing neural networks' behavior, most notably the information bottleneck theory. However, estimating mutual information is a notoriously tricky task, especially for high-dimensional stochastic variables. Recently, mutual information neural estimation (MINE) was proposed as a non-parametric method to estimate mutual information for continuous variables without discretization. Unfortunately, MINE also produces significant errors for high-dimensional variables.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views